OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH MEASURES IN PRE-ENGINEERED STEEL BUILDINGS CONSTRUCTION
The rapid growth of the industrial construction sector necessitates a strong focus on occupational safety and health (OSH) in pre-engineered steel buildings construction. OSH is a critical factor determining the success of any project. According to statistics from the Ministry of Construction, industrial construction accidents accounted for 31.5% of all workplace accidents in 2023. This article provides essential OSH measures to help companies create a safe and efficient work environment.

1. Overview of Occupational Safety and Health in Pre-Engineered Steel Buildings Construction
1.1. Characteristics of Pre-Engineered Steel Buildings Construction
Pre-engineered steel buildings construction is a complex process requiring close coordination between various stages. Each stage presents potential occupational safety and health risks that must be identified and controlled with meticulous safety measures.
The Erection Process at Triviet Steel Buildings:
- Delivery to site
- Anchor bolts installation
- Steel structure installation
- Roof panels installation
- Wall panels installation
- Finish and handover


1.2. Occupational Accident Statistics and Analysis
According to statistics from the Department of Occupational Safety and Health (Ministry of Labour, Invalids and Social Affairs), there were 7,394 workplace accidents in 2023.
Categorization by Severity:
- Fatal Accidents: 15%
- Serious Injuries: 35%
- Minor Injuries: 50%
Categorization by Cause:
- Falls from Height: 65%
- Machinery and Equipment Accidents: 25%
- Electrocution: 5%
- Other Causes: 5%

1.3. Key Occupational Safety and Health Regulations and Standards
Laws:
- Law No. 84/2015/QH13 (2015): This is the most important law, comprehensively covering occupational safety and health issues. It defines the rights and obligations of employees and employers, safety and health measures, supervision and inspection procedures, and penalties for violations.
- Law No. 45/2019/QH14: While not specifically an occupational safety and health law, the Labor Code contains several related provisions, particularly concerning working hours, rest periods, social insurance, and compensation for workplace accidents.
Decrees:
- Decree No. 44/2016/NĐ-CP: This decree details several articles of the OSH Law. It provides specific guidance on developing and implementing OSH plans, training, managing equipment and materials with strict safety requirements, and OSH assessments and acceptance procedures.
- Decree No. 145/2020/NĐ-CP: This decree stipulates administrative penalties for violations in labor, social insurance, and overseas employment. It specifies fines for OSH violations.
Standards:
In addition to the legal documents mentioned above, several national and international OSH standards should be consulted and applied, such as:
- TCVN ISO 45001:2018: Occupational health and safety management systems – Requirements with guidance for use

2. 11 Occupational Safety and Health Measures in Pre-Engineered Steel Building Construction
2.1. Develop And Implement Detailed Occupational Safety And Health Procedures
A detailed and systematic OSH procedure is the foundation for all safe construction activities. This procedure should be based on the current OSH Law, international standards, and actual site conditions.
The procedure must cover all phases of pre-engineered steel building construction, from transportation and erection to welding, painting, roofing, and project completion. Each stage should have specific instructions on potential hazards, preventive measures, incident handling procedures, and individual responsibilities.
After issuance, the procedure should be widely disseminated, thoroughly explained to all workers through training, and regularly reviewed, evaluated, and updated.

2.2. Occupational Safety and Health Training and Awareness
OSH training goes beyond equipping workers with knowledge and skills; it cultivates a sense of responsibility and proactive safety awareness. A comprehensive training program should encompass:
- OSH Laws and Regulations: Provide a thorough understanding of the OSH Law, relevant decrees, and circulars, ensuring workers know their rights and responsibilities.
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment: Train workers to identify potential hazards in each construction phase, assess risk levels, and propose preventive measures.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Use: Provide training on the correct use, maintenance, and inspection of PPE such as helmets, safety harnesses, goggles, gloves, and safety shoes.
- Emergency Procedures and First Aid: Equip workers with skills to handle emergencies like workplace accidents, fires, collapses, and provide basic first aid.
Training should be conducted regularly and systematically, combining theory and practice, to ensure all workers possess the necessary knowledge and skills.

2.3. Safe Operation of Heavy Machinery
Heavy machinery plays a vital role in pre-engineered steel building construction, but it also presents significant accident risks if not operated correctly. Strict adherence to the following regulations is essential:
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Ensure all machinery is in optimal working condition and safe to operate.
- Professional Operator Training: Only trained personnel with valid operating certifications should be allowed to operate heavy machinery.
- Adherence to Operating Procedures: Follow all operating steps and conduct safety checks before starting any machinery.
- Safe Operating Zones: Clearly demarcate and signpost machinery operating areas to prevent unauthorized access.
- Ground Condition Assessment: Conduct thorough ground surveys and reinforce foundations in areas with weak soil conditions before operating heavy machinery.

2.4. Construction Material Management
Systematic and organized material management not only saves costs but also minimizes accident risks. Key considerations include:
- Designated Storage Areas: Allocate separate, dry, and well-ventilated storage areas away from the main construction zone.
- Organized Storage: Materials should be stacked according to regulations, ensuring stability and preventing collapse. Use shelves and pallets to support heavy materials.
- Clear Signage: Use clear signage to warn of potential hazards and guide movement within the material storage area.
- Regular Inspections: Inspect materials regularly, discarding damaged or substandard items.
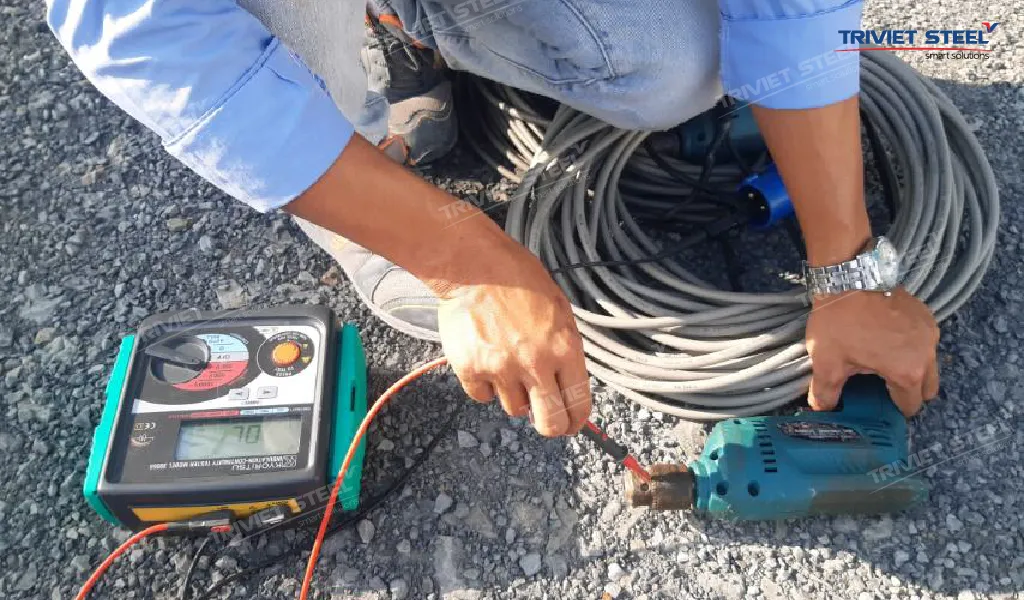

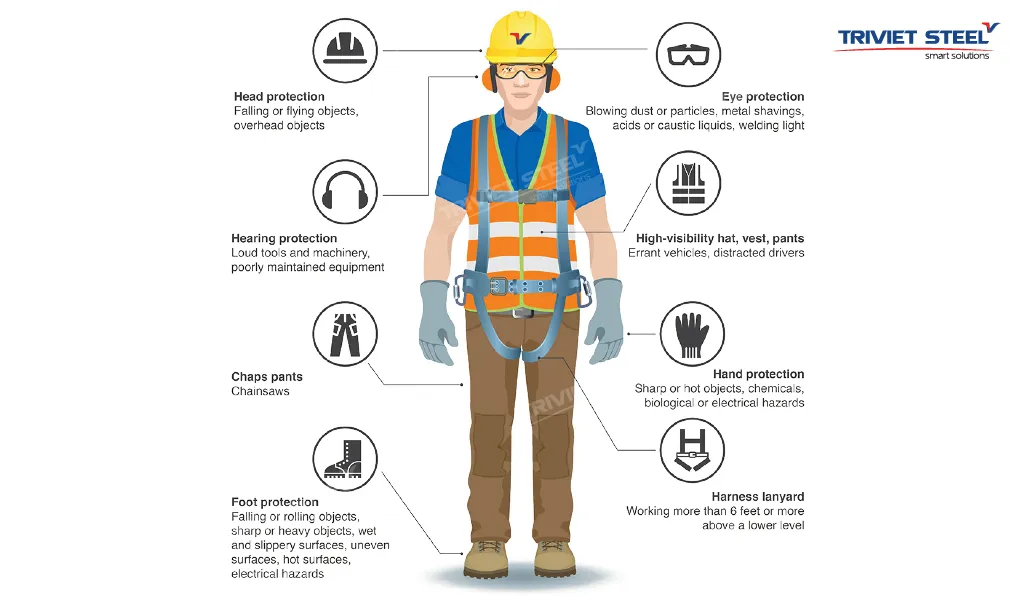
2.5. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Management and Provision
PPE acts as essential armor, protecting workers from workplace hazards. In pre-engineered steel building construction, providing appropriate PPE for each specific task is crucial. Essential PPE includes:
- Helmets (Hard Hats)
- Safety Glasses/Goggles
- Ear Plugs/Muffs
- Respirators/Face Masks
- Safety Gloves
- Safety Shoes/Boots
- Safety Harnesses
- Protective Clothing
Important Considerations:
- PPE must be regularly inspected and replaced when damaged.
- Workers must be trained on the proper use and maintenance of PPE.
- Employers are responsible for providing PPE to employees free of charge.
2.6. Guardrails and Safety Barriers
Guardrails and safety barriers are passive but highly effective safety measures, especially in preventing falls from heights. In pre-engineered steel building construction, install these safeguards in the following areas:
- Working Platforms and Scaffolding: Install sturdy guardrails that meet height regulations.
- Roofs: Install guardrails around roof edges.
- Excavations and Pits: Erect barriers around excavations and pits.
- Machinery Operating Areas: Use barriers to restrict access to machinery operating areas to authorized personnel only.
Important Considerations:
- Guardrails and barriers must be constructed from durable materials to ensure stability.
- Regularly inspect guardrails and barriers, repairing or replacing them as needed.

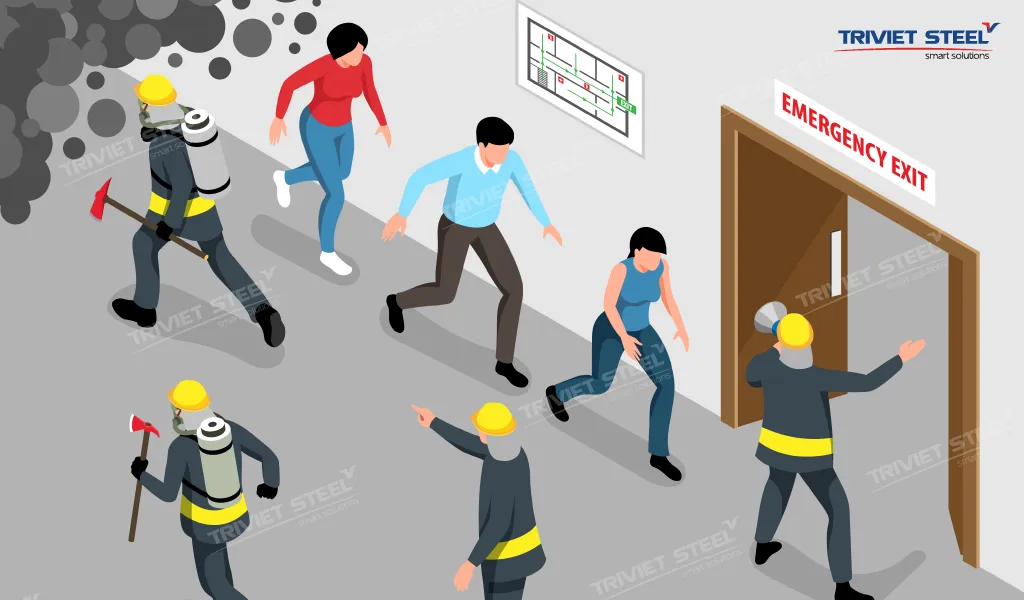
2.7. Emergency Exit Usage Guidelines
In any construction project, preparedness for emergencies such as fires, earthquakes, or other incidents is critical. Emergency exits play a key role in ensuring the safety and evacuation of workers. Implementing occupational safety and health measures for emergency exits is essential for worker protection
- Design and Layout: Emergency exits should be clearly designed and unobstructed by equipment or materials. They must be placed in convenient locations to ensure quick evacuation.
- Marking and Signage: Emergency exits should be marked with visible signs and guide lights, easily seen even in low-light conditions. Use glow-in-the-dark paint to enhance visibility in the dark.
- Emergency Lighting System: Install an emergency lighting system powered by backup electricity to ensure visibility of exit routes during power outages.
- Training and Drills: Regularly conduct emergency evacuation training and drills for workers. Provide instructions on how to use fire extinguishers and how to safely move through crowds during an evacuation.
- Inspections and Maintenance: Perform regular checks of emergency exit systems to ensure they are fully operational. Inspect exit doors, lighting, signage, and firefighting equipment, and perform maintenance or replacements as needed.
- Communication Systems: Ensure that communication systems are functional to provide timely alerts and guidance to workers during emergencies.

2.8. Effective Workforce Management
Physical and mental exhaustion can lead to a loss of focus, increasing the risk of workplace accidents. Effective workforce management not only helps prevent burnout but also optimizes productivity. Here are some occupational safety and health measures for workforce management:
- Detailed Workforce Planning: Allocate workers appropriately based on the workload and their skills. Avoid overburdening or understaffing key construction phases.
- Limit Overtime Work: Ensure that workers have adequate rest periods, allowing them to recover and maintain focus. Follow strict regulations on working hours.
- Job Rotation: Rotate workers between different tasks to prevent monotony and reduce stress.
- Training and Development: Invest in ongoing training and skill development to help workers enhance their capabilities and confidence on the job.
- Mental Health Support: Foster a positive work environment that supports workers in managing stress and dealing with work-related pressures.
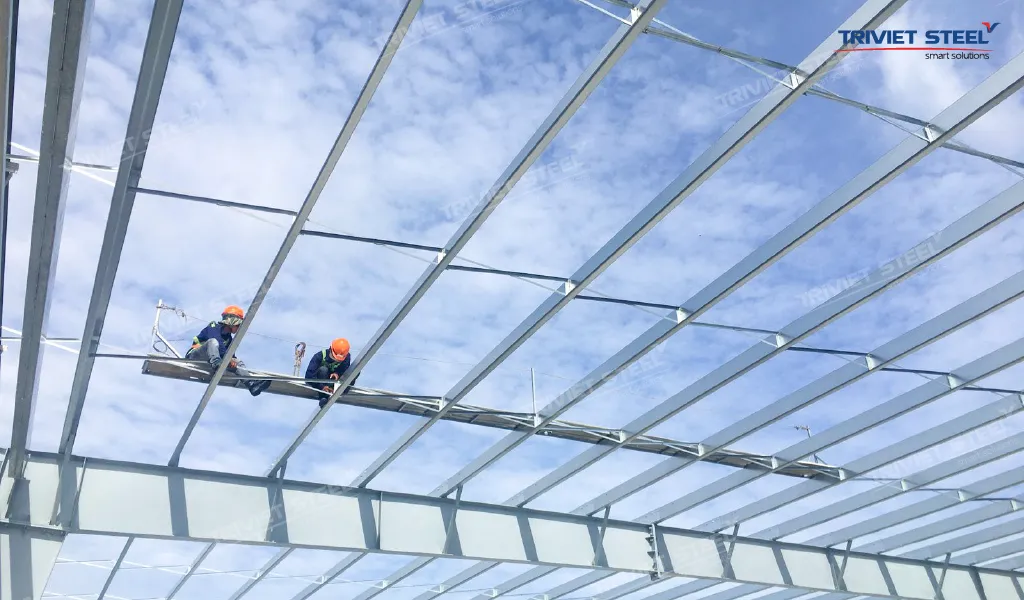

2.9. Emergency Medical Supplies and First Aid
Workplace accidents can occur unexpectedly. Having adequate emergency medical supplies and trained first aid personnel is crucial for minimizing harm.
- First Aid Kits: Place clearly marked and easily accessible first aid kits in strategic locations, stocked with essential supplies like antiseptics, bandages, pain relievers, burn cream, etc.
- Trained First Aid Personnel: Train designated personnel in first aid and CPR to provide immediate assistance in case of accidents.
- Accident Response Procedures: Establish clear accident response procedures, including first aid steps and transportation of injured workers to medical facilities.
- Emergency Contact Information: Display emergency contact numbers (ambulance, fire department, etc.) prominently.

2.10. Maintaining a Clean and Organized Worksite
A clean and organized worksite not only promotes a professional image but also reduces accident risks.
- Debris Removal: Regularly remove materials, debris, and tools from work areas and walkways.
- Organized Material Storage: Store materials neatly in designated areas.
- Clear Walkways: Ensure walkways are clear of obstructions.
- Regular Cleaning: Implement a regular cleaning schedule to remove dust, debris, and potential hazards.
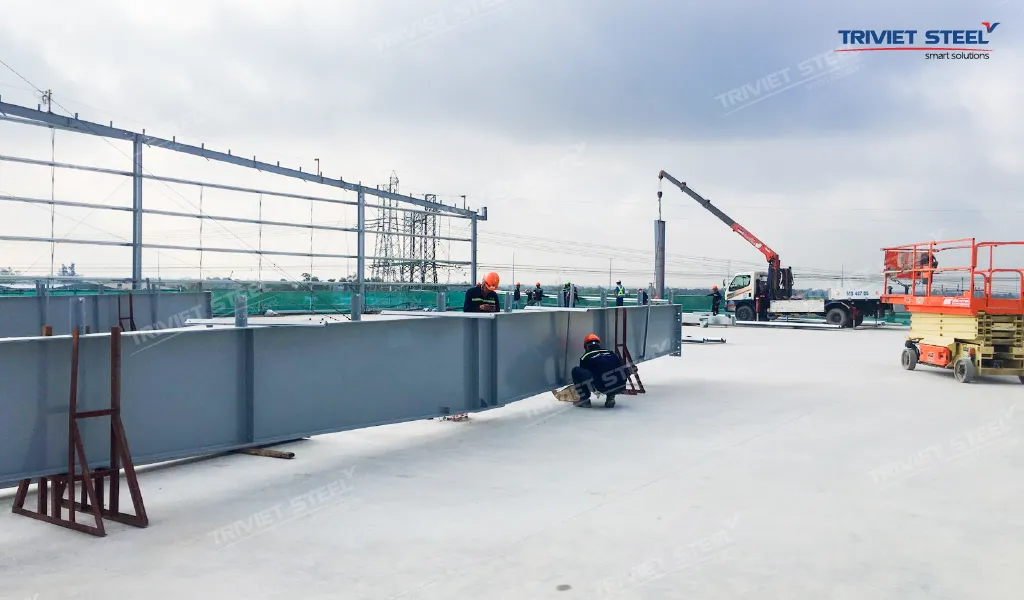

2.11. Regular Equipment and Machinery Maintenance
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections and maintenance for all equipment and machinery. These inspections should be conducted by qualified personnel and documented meticulously.
- Prompt Repairs: Address any damage or malfunctions immediately. Avoid using faulty equipment.
- Operator Training: Train workers on the proper operation and maintenance of equipment and machinery.
- Proper Storage: Store equipment and machinery in a dry, ventilated area, protected from water and chemicals.
- Adhere to Manufacturer’s Instructions: Strictly follow the manufacturer’s operating and maintenance instructions.

>> READ MORE: 10-STEP PROCESS FOR MANUFACTURING STEEL STRUCTURES <<
3. The Importance of Occupational Safety and Health Measures
OSH is a core element of any construction activity, especially in pre-engineered steel building projects. A safe work environment offers numerous practical benefits:
- Worker Protection: This is the paramount objective, safeguarding workers from accidents, occupational illnesses, and protecting their health and lives.
- Increased Productivity: When workers feel safe and secure, they are more focused and productive.
- Cost Reduction: Accidents incur significant costs, including medical expenses, compensation, repairs, and equipment replacement. Investing in OSH mitigates these costs.
- Enhanced Company Reputation: Companies prioritizing OSH demonstrate social responsibility, building trust with clients and partners.
- Legal Compliance: Ensuring OSH is a legal obligation for all businesses. Compliance prevents penalties and legal action.

4. Challenges in Ensuring Occupational Safety and Health
Despite the recognized importance of OSH, practical implementation in pre-engineered steel building construction faces several challenges:
- Complex Work Nature: The work involves multiple complex stages, heavy machinery, working at heights, and often challenging environmental conditions.
- Worker Awareness: Some workers may lack awareness of safety procedures and fail to comply with regulations, increasing accident risks.
- Project Deadlines: Pressure to meet deadlines can sometimes lead to safety being compromised.
- Lax Supervision: Inadequate safety management and ineffective supervision can contribute to accidents.
- Insufficient Investment: Some companies may underinvest in OSH, providing inadequate or substandard PPE.
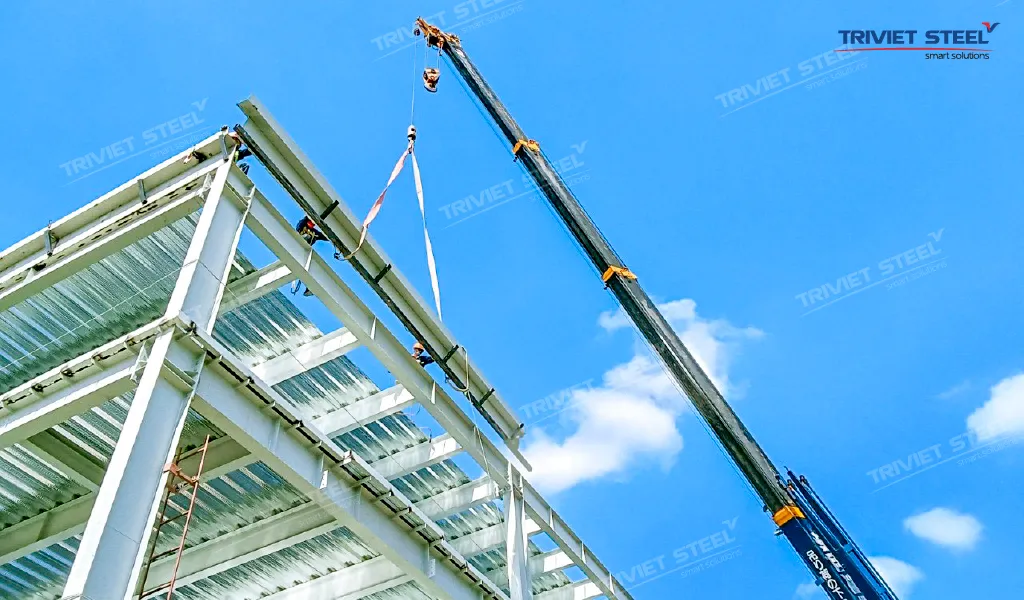

5. Fundamental Principles of Occupational Safety and Health
To ensure OSH in pre-engineered steel building construction, adhere to these fundamental principles:
- Prevention: Proactive accident prevention is the most effective approach. Identify, assess risks, and implement appropriate preventive measures.
- Compliance: Workers must strictly adhere to OSH regulations, use PPE correctly, and follow established operating procedures.
- Training and Education: Provide regular OSH training and education to equip workers with the necessary knowledge and skills.
- Inspection and Supervision: Regularly inspect and supervise OSH practices, promptly identifying and addressing potential hazards.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously evaluate and improve the OSH management system to enhance effectiveness and adapt to changing conditions.
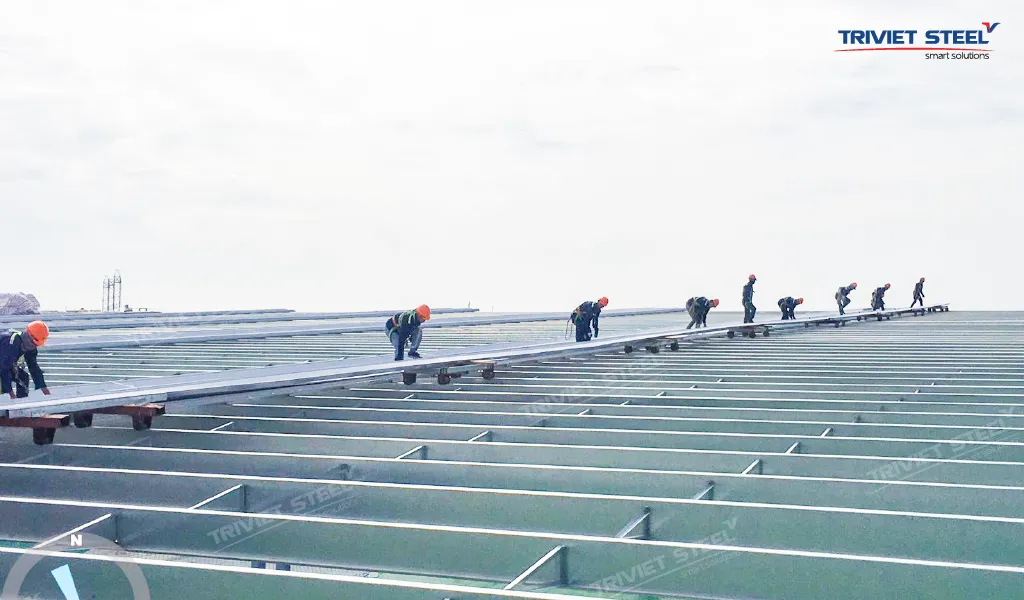

6. Conclusion
Occupational safety and health in pre-engineered steel building construction is a multifaceted system with interconnected elements. Implementing comprehensive safety measures, from PPE and workforce management to emergency preparedness, site hygiene, and equipment maintenance, creates a secure work environment, protects worker health, and enhances productivity.
Investing in OSH is an investment in the sustainable development of your business. Beyond the measures discussed, staying updated on OSH knowledge and adopting new technologies are crucial for improving safety outcomes.
Ultimately, OSH is the shared responsibility of both the company and individual employees. Each worker must prioritize their own safety and that of their colleagues, diligently adhering to OSH regulations.

7. Triviet Steel Buildings – Smart Solutions for Pre-Engineered Steel Buildings
Triviet Steel Buildings is a leading provider of pre-engineered steel buildings in Vietnam. With 20 years of experience, Triviet Steel has successfully constructed thousands of projects nationwide, ranging from residential homes and factories to warehouses and commercial buildings.
Triviet Steel Buildings is committed to providing clients with smart, high-quality, and cost-competitive pre-engineered buildings solutions. Our experienced team of engineers and architects can meet diverse client needs, from simple to complex projects.
 English
English Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt